
Google has released Chrome 79 today, December 10th, 2019, to the Stable desktop channel and it comes with bug fixes, new features, and 51 security fixes. Included are new features such as Tab Freeze, back-forward cache, and security enhancements such as improved phishing protection and compromised password alerts.
Windows, Mac, and Linux desktop users can upgrade to Chrome 79.0.3945.79 by going to Settings -> Help -> About Google Chrome and the browser will automatically check for the new update and install it when available. Android and iOS users can update Chrome from their respective App stores.
With Chrome 79 now being promoted to the Stable channel, Chrome 80 will soon (December 19th) be the Beta version and Chrome 81 will be the Canary version.
A full list of all changes in this release is available in the Chrome 79 changelog.
Improved Phishing Protection
Chrome 79 includes new security enhancements that protect users from phishing landing pages by using real-time and expanded predictive phishing protection.
When you browse to web sites, Google will check a local list of known phishing sites to determine if a warning should be issued. The problem is that this list is updated every 30 minutes, so new phishing sites can slip through the cracks and users will not be warned.
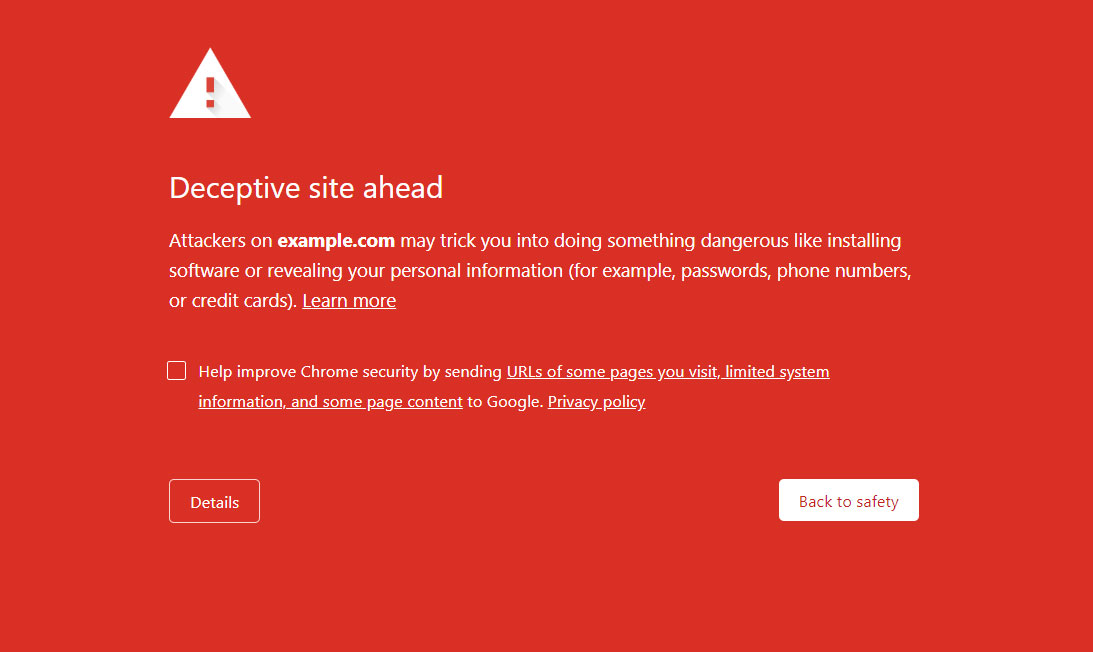
With real-time phishing protection, Google will compare a visited URL with a known list of safe sites that is stored on your computer. If the URL does not exist in that list, Chrome will query SafeBrowsing to determine if the site is a known phishing site.
Google states that this change has increased the blocking of new phishing sites by 30%.
This feature will be rolled out first to users who have opted-in to “Make searches and browsing better” and more users at a later date.
The other new phishing protection added in Chrome 79 is called predictive phishing protection, which alert you when you enter your credentials on a known phishing site.
If it is determined you entered your credentials on a malicious site, Chrome will display an alert advising you to change the password for that account immediately.
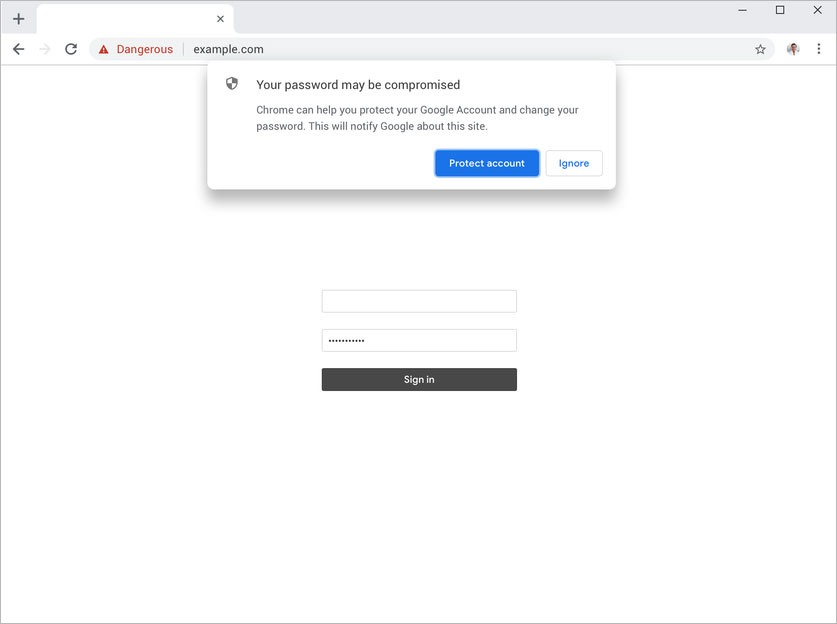
Compromised Password alerts
With Chrome 79, Google is rolling out a feature that will display an alert when logging into a site if your login credentials were compromised during a data breach.

Google will determine if your logins are compromised by comparing hashed copies of your username and password with hashed credentials found in data breaches using the following steps:
-
Whenever Google discovers a username and password exposed by another company’s data breach, we store a strongly hashed and encrypted copy of the data on our servers with a secret key known only to Google.
-
When you sign in to a website, Chrome will send a strongly hashed copy of your username and password to Google encrypted with a secret key only known to Chrome. No one, including Google, is able to derive your username or password from this encrypted copy.
-
In order to determine if your username and password appears in any breach, we use a technique called private set intersection with blinding that involves multiple layers of encryption. This allows us to compare your encrypted username and password with all of the encrypted breached usernames and passwords, without revealing your username and password, or revealing any information about any other users’ usernames and passwords. In order to make this computation more efficient, Chrome sends a 3-byte SHA256 hash prefix of your username to reduce the scale of the data joined from 4 billion records, down to 250 records while still ensuring your username remains anonymous.
-
Only you discover if your username and password have been compromised. If they have been compromised, we strongly encourage you to change your password.
TLS 1.0 and 1.1 to be marked as Not Secure
Chrome 79 will start marking the insecure TLS 1.0 and 1.1 protocols as 'Not Secure' starting on January 13th, 2020.
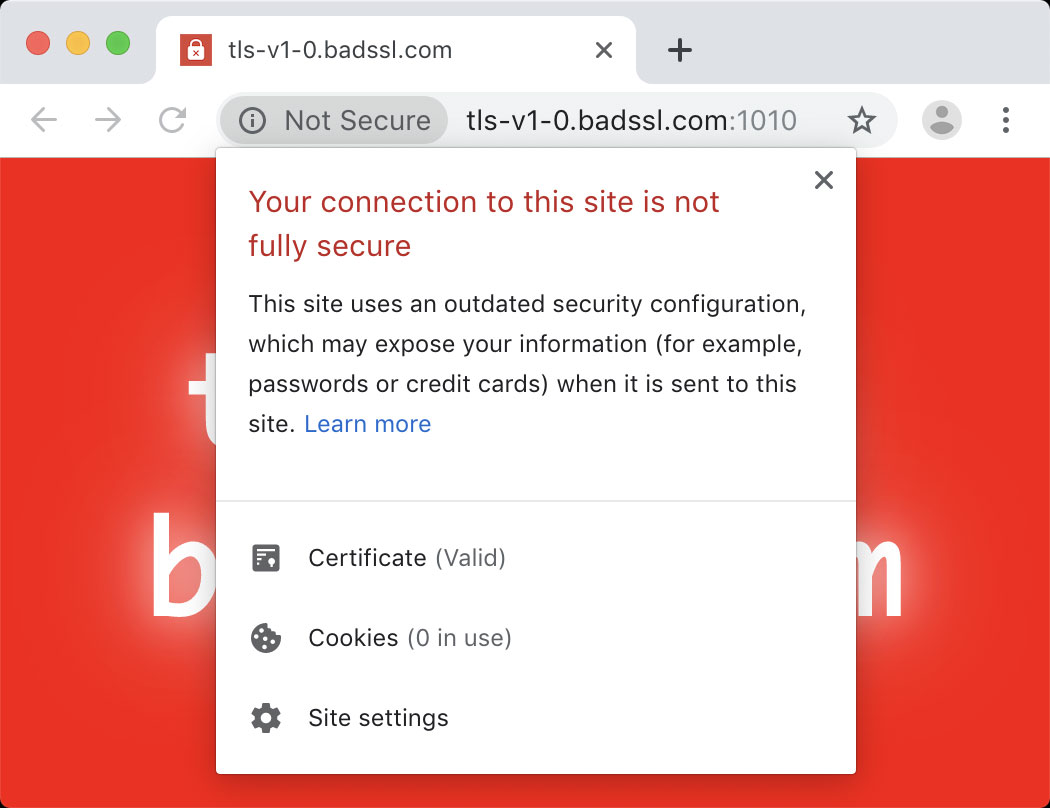
This is a coordinated action between all major browser developers including Google, Apple, Microsoft, and Mozilla.
New features being tested behind flags
In addition to the new features that are automatically enabled in Chrome 79, with this release we also have some features hidden behind flags.
Proactive Tab Freeze
The Proactive Tab Freeze feature will freeze tabs that have not been used for 5 minutes in order to reduce battery usage and memory/CPU utilization.
Users can enable this flag by going to the chrome://flags/#proactive-tab-freeze URL in Chrome.
Back-forward cache
Google is introducing a back-forward cache that will cache an entire page when you navigate away from it. This will allow users to quickly go back and forth between pages without having to load resources each time.
Google states that this feature makes "navigating back and forth very fast." This feature can be enabled at the chrome://flags/#back-forward-cache URL.

51 security vulnerabilities fixed
The release of Chrome 79 fixes 51 security vulnerabilities, with the following discovered by external researchers:
- Critical CVE-2019-13725: Use after free in Bluetooth. Reported by Gengming Liu, Jianyu Chen at Tencent Keen Security Lab on 2019-11-15
- Critical CVE-2019-13726: Heap buffer overflow in password manager. Reported by Sergei Glazunov of Google Project Zero on 2019-11-21
- High CVE-2019-13727: Insufficient policy enforcement in WebSockets. Reported by @piochu on 2019-03-21
- High CVE-2019-13728: Out of bounds write in V8. Reported by Rong Jian and Guang Gong of Alpha Lab, Qihoo 360 on 2019-11-14
- High CVE-2019-13729: Use after free in WebSockets. Reported by Zhe Jin(??),Luyao Liu(???) from Chengdu Security Response Center of Qihoo 360 Technology Co. Ltd on 2019-11-16
- High CVE-2019-13730: Type Confusion in V8. Reported by Wen Xu of SSLab, Georgia Tech on 2019-11-27
- High CVE-2019-13732: Use after free in WebAudio. Reported by Sergei Glazunov of Google Project Zero on 2019-11-12
- High CVE-2019-13734: Out of bounds write in SQLite. Reported by "Team 0x34567a61" @Xbalien29 @leonwxqian on 2019-11-16
- High CVE-2019-13735: Out of bounds write in V8. Reported by Gengming Liu and Zhen Feng from Tencent Keen Lab on 2019-11-16
- High CVE-2019-13764: Type Confusion in V8. Reported by Wen Xu of SSLab, Georgia Tech on 2019-11-26
- Medium CVE-2019-13736: Integer overflow in PDFium. Reported by Anonymous on 2019-11-03
- Medium CVE-2019-13737: Insufficient policy enforcement in autocomplete. Reported by Mark Amery on 2019-10-12
- Medium CVE-2019-13738: Insufficient policy enforcement in navigation. Reported by Johnathan Norman and Daniel Clark of Microsoft Edge Team on 2019-10-23
- Medium CVE-2019-13739: Incorrect security UI in Omnibox. Reported by xisigr of Tencent's Xuanwu Lab on 2018-03-22
- Medium CVE-2019-13740: Incorrect security UI in sharing. Reported by Khalil Zhani on 2019-09-19
- Medium CVE-2019-13741: Insufficient validation of untrusted input in Blink. Reported by Michal Bentkowski of Securitum on 2019-10-07
- Medium CVE-2019-13742: Incorrect security UI in Omnibox. Reported by Khalil Zhani on 2019-10-24
- Medium CVE-2019-13743: Incorrect security UI in external protocol handling. Reported by Zhiyang Zeng of Tencent security platform department on 2017-08-10
- Medium CVE-2019-13744: Insufficient policy enforcement in cookies. Reported by Prakash (@1lastBr3ath) on 2018-06-18
- Medium CVE-2019-13745: Insufficient policy enforcement in audio. Reported by Luan Herrera (@lbherrera_) on 2019-08-05
- Medium CVE-2019-13746: Insufficient policy enforcement in Omnibox. Reported by David Erceg on 2019-09-02
- Medium CVE-2019-13747: Uninitialized Use in rendering. Reported by Ivan Popelyshev and André Bonatti on 2019-10-26
- Medium CVE-2019-13748: Insufficient policy enforcement in developer tools. Reported by David Erceg on 2019-08-14
- Medium CVE-2019-13749: Incorrect security UI in Omnibox. Reported by Khalil Zhani on 2019-10-03
- Medium CVE-2019-13750: Insufficient data validation in SQLite. Reported by "Team 0x34567a61" @Xbalien29 @leonwxqian on 2019-11-16
- Medium CVE-2019-13751: Uninitialized Use in SQLite. Reported by "Team 0x34567a61" @Xbalien29 @leonwxqian on 2019-11-16
- Medium CVE-2019-13752: Out of bounds read in SQLite. Reported by Wenxiang Qian of Tencent Blade Team on 2019-11-16
- Medium CVE-2019-13753: Out of bounds read in SQLite. Reported by Wenxiang Qian of Tencent Blade Team on 2019-11-16
- Low CVE-2019-13754: Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions. Reported by Cody Crews on 2014-12-16
- Low CVE-2019-13755: Insufficient policy enforcement in extensions. Reported by Masato Kinugawa on 2017-02-25
- Low CVE-2019-13756: Incorrect security UI in printing. Reported by Khalil Zhani on 2017-04-05
- Low CVE-2019-13757: Incorrect security UI in Omnibox. Reported by Khalil Zhani on 2018-09-17
- Low CVE-2019-13758: Insufficient policy enforcement in navigation. Reported by Khalil Zhani on 2019-06-28
- Low CVE-2019-13759: Incorrect security UI in interstitials. Reported by Wenxu Wu (@ma7h1as) of Tencent Security Xuanwu Lab on 2018-11-05
- Low CVE-2019-13761: Incorrect security UI in Omnibox. Reported by Khalil Zhani on 2019-09-10
- Low CVE-2019-13762: Insufficient policy enforcement in downloads. Reported by csanuragjain (@csanuragjain) on 2019-09-16
- Low CVE-2019-13763: Insufficient policy enforcement in payments. Reported by weiwangpp93 on 2019-10-05



Post a Comment Community Rules
You need to login in order to post a comment
Not a member yet? Register Now