Politics
Political Longshots That Caught America by Surprise

Millions of Americans rely on polls and the media to gauge the direction of political elections. Politics are sometimes unpredictable though, and on occasion, election outcomes can defy conventional wisdom.
These surprises, known as political longshots, are scattered throughout American political history. As time winds down to the 59th U.S. presidential election in November, today’s visual article from PredictIt goes back in time to showcase moments when polls, media outlets, and the American public were left stunned.
The Truman Show

What Happened?
As elections approached in 1948, incumbent Harry Truman led a struggling Democratic party.
Not only had they lost control of both chambers of Congress two years prior, they also faced internal divide over Truman’s civil rights initiatives. To make matters worse, Truman’s approval rating in June 1948 sat at just 39%.
Pollsters and the media were unanimous in declaring Republican Thomas Dewey the next president, but this didn’t discourage Truman from running a tactical campaign which featured:
- Clear demographic focus: Truman campaigned heavily in rural communities where working-class citizens felt neglected.
- Populist messaging: Truman often attacked Republicans, pinning them with the blame for a range of issues.
Despite being overlooked by many, Truman went on to claim a decisive victory. This caused one of the most famous media blunders in U.S. history—with high confidence in the polls, editors at the Chicago Daily Tribune prematurely reported Dewey as the winner of the election.
We stopped polling a few weeks too soon. We had been lulled into thinking that nothing much changes in the last few weeks of the campaign.
—George Gallup Jr.
Pollsters took a hit to their credibility, but used the opportunity to refine their methods. They extended the deadlines of polls and, over time, began using a methodology known as random sampling. This replaced quota sampling, a methodology prone to bias because it questioned a predetermined number of people from certain ethnic and age groups.
Murkowski’s Comeback

What Happened?
After losing the Republican primary to Joe Miller, incumbent senator Lisa Murkowski decided to run in 2010 as a write-in candidate. A somewhat unique aspect of American politics, a write-in candidate is one whose name does not appear on the ballot, and instead needs to be written in by the voter directly.
Miller, the Republican nominee, was supported by the Tea Party movement and former Alaskan governor Sarah Palin. All momentum seemed to be in his favor, according to polls conducted roughly a month ahead of election day:
| Poll | Date Administered | Joe Miller (R) | Lisa Murkowski (R) | Scott McAdams (D) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raasmussen Reports | Sept. 19, 2010 | 42% | 27% | 25% |
| Moore Research | Sept. 23-27, 2010 | 43% | 18% | 28% |
| CNN, Time, Opinion Research | Sept. 24-28, 2010 | 38% | 36% | 22% |
Source: Rasmussen Reports, Moore Research, CNN/Time/Opinion Research
Despite Miller’s lead in the polls, Murkowski’s write-in campaign was able to capitalize on the state’s significant number of independent voters. On election day, Murkowski collected 101,091 write-in votes—a comfortable margin above Miller’s 90,839 votes.
[I]n our state, we have got over 54 percent of the electorate that chooses not to align themselves with any party at all, not Republican, not Democratic, not green, not anything.
—Lisa Murkowski
Miller challenged 8,000 write-in votes on the basis of name misspellings, but his claims were rejected by the Alaska Superior Court—perfect spelling on write-in ballots is not required if the voter’s intent is clear.
The Trump Train
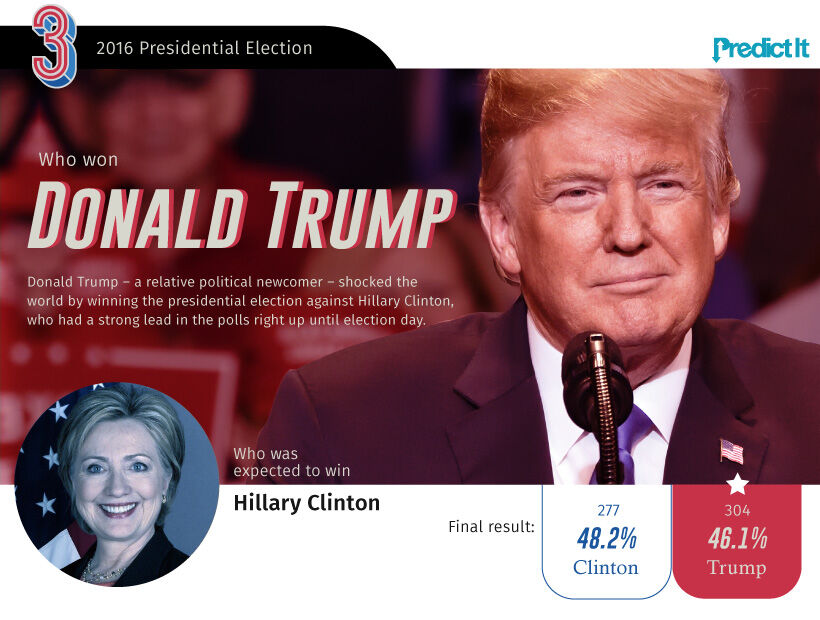
What Happened?
Donald Trump’s 2016 victory will likely top the list as one of the most shocking political events of our time. As election day approached, many of America’s mainstream media outlets pointed to a decisive Clinton victory.
| Outlet | Clinton | Trump |
|---|---|---|
| L.A. Times by electoral count | 352 | 186 |
| Fox News by electoral count | 274 | 215 |
| New York Times by chance of winning | 85% | 15% |
| CNN by chance of winning | 91% | 9% |
Source: The Wrap, CNN
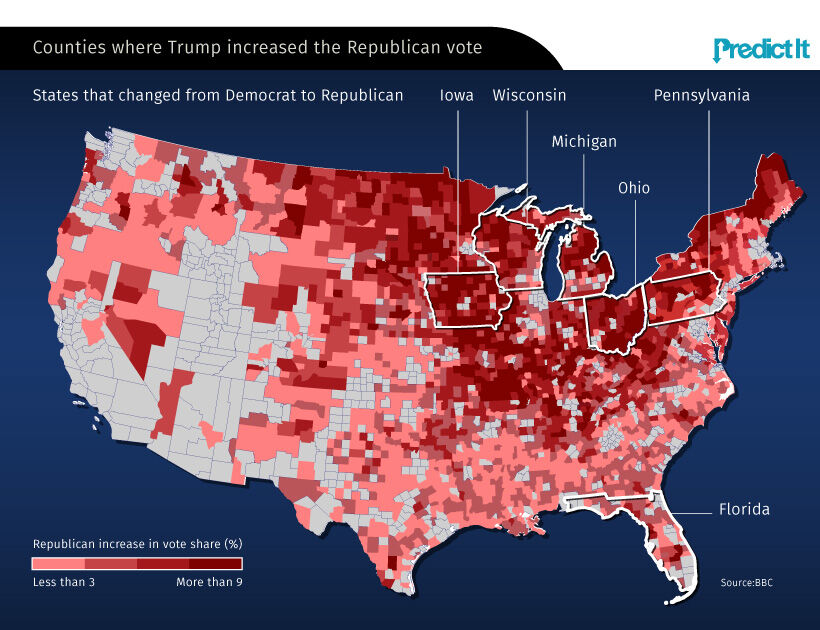
While Trump’s rhetoric was largely opposed in urban regions (which often lean Democrat), the media failed to recognize that his message was resonating in America’s industrial Midwest. One potential explanation for this is that the region’s manufacturing jobs had been drying up, causing workers to feel abandoned by the existing political establishment.
This led to a number of Democrat-controlled states flipping Republican, and was a critical force for propelling Trump to the White House.
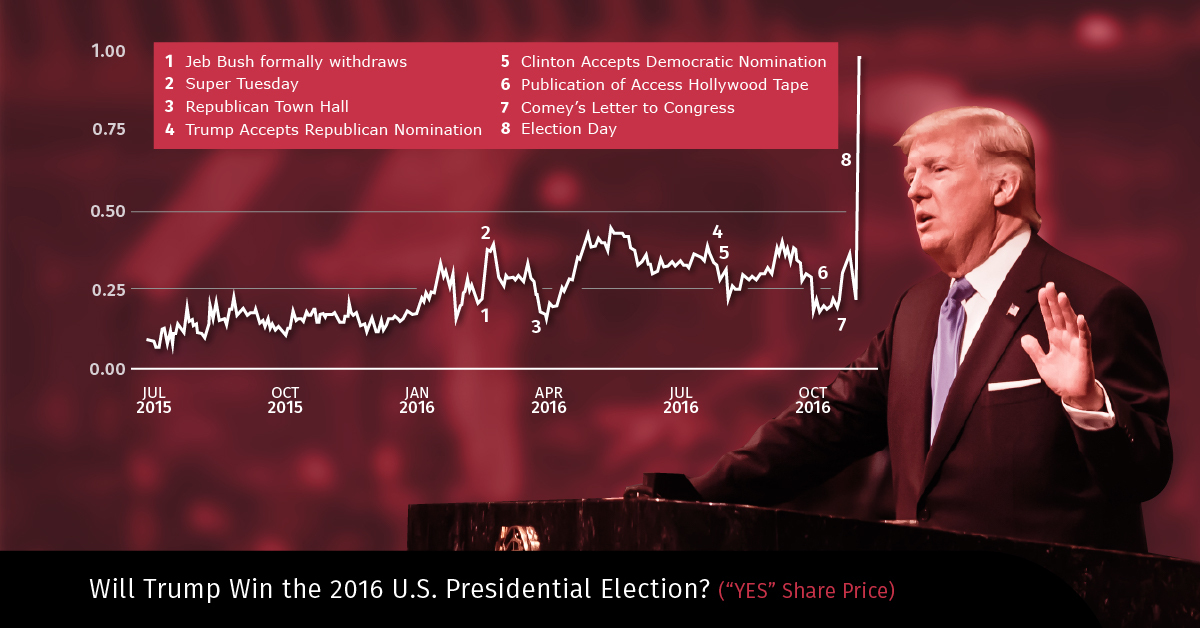
In PredictIt’s market, Will Trump Win the 2016 Presidential Election, traders also underestimated Trump’s chances of winning. Throughout the entire campaign phase, Trump’s “yes” shares failed to break past the 50 cents marker.
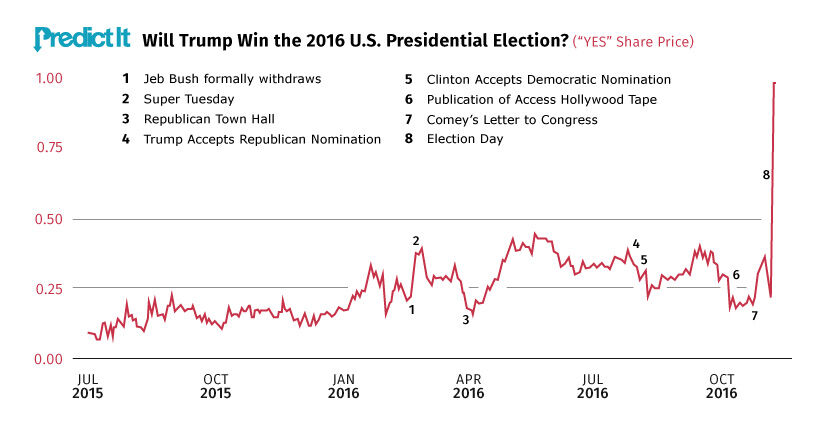
Source: Predictit
Share prices climbed 64% after FBI Director James Comey released his letter regarding the Clinton email investigation, but these gains were erased in the days leading up to elections. It wasn’t until November 8th, election day, that the prediction market swung by an incredible 345% in favor of Trump.
The Rise of AOC

What Happened?
The biggest surprise from the 2018 midterm primaries was Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez’s (AOC) victory over incumbent Joseph Crowley in New York’s 14th Congressional District. That’s because the two candidates were nearly complete opposites of one another:
| Metric | Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez | Joseph Crowley |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 28 | 56 |
| Past Political Experience | Organizer for Bernie Sanders' 2016 presidential campaign | U.S. Representative from New York's 14th congressional district (1999-2019) |
| Fundraising | $300,000 | $3,354,370 |
Source: abc news
AOC led a grassroots campaign appealing to the district’s ethnically diverse population, which many believed Crowley could not relate with. Her platform included:
Also lending to the surprise factor was AOC’s relatively sparse media coverage. Because her campaign was largely operated through social media platforms such as Twitter and Instagram, it flew under the radar of traditional political media coverage.
The traditional media pay attention to one metric—money—but there should be other considerations: number of volunteers, social-media engagement, small-dollar donations.
—Dave Weigel, Washington Post
AOC would go on to win New York’s 14th Congressional District in the 2018 midterm election, defeating Republican Anthony Pappas with 110,318 votes to 19,202, to become the youngest woman to ever serve in the U.S. Congress. More recently, she secured her re-election in the 2020 Democratic primaries. This time, however, it comes as less of a surprise.
What’s Next?
The very definition of a longshot means that they are difficult to quantify and predict.
However, one potential longshot in the making may be 21-time Grammy Award winner Kanye West, who announced his intention to run for president on July 4th. While he hasn’t taken any official steps towards running as an independent candidate, he has garnered the support of notable figures like Tesla CEO Elon Musk. West first declared his interest in the presidency during an acceptance speech at the 2015 MTV Video Music Awards.
Looking further down the road, Democratic presidential nominee Joe Biden has still not declared his running mate. Much is at stake for Democrats hoping to deny Trump a second term, and the VP nominee will likely play a significant role in how the party performs. Biden has a long list of candidates that, for the first time in history, predominantly features women of color.
Speculation is ramping up as the 2020 presidential elections approach. While it’s difficult to say when politics will surprise us again, more longshots are sure to be in store.
Economy
The Bloc Effect: International Trade with Geopolitical Allies on the Rise
Rising geopolitical tensions are shaping the future of international trade, but what is the effect on trading among G7 and BRICS countries?

The Bloc Effect: International Trade with Allies on the Rise
International trade has become increasingly fragmented over the last five years as countries have shifted to trading more with their geopolitical allies.
This graphic from The Hinrich Foundation, the first in a three-part series covering the future of trade, provides visual context to the growing divide in trade in G7 and pre-expansion BRICS countries, which are used as proxies for geopolitical blocs.
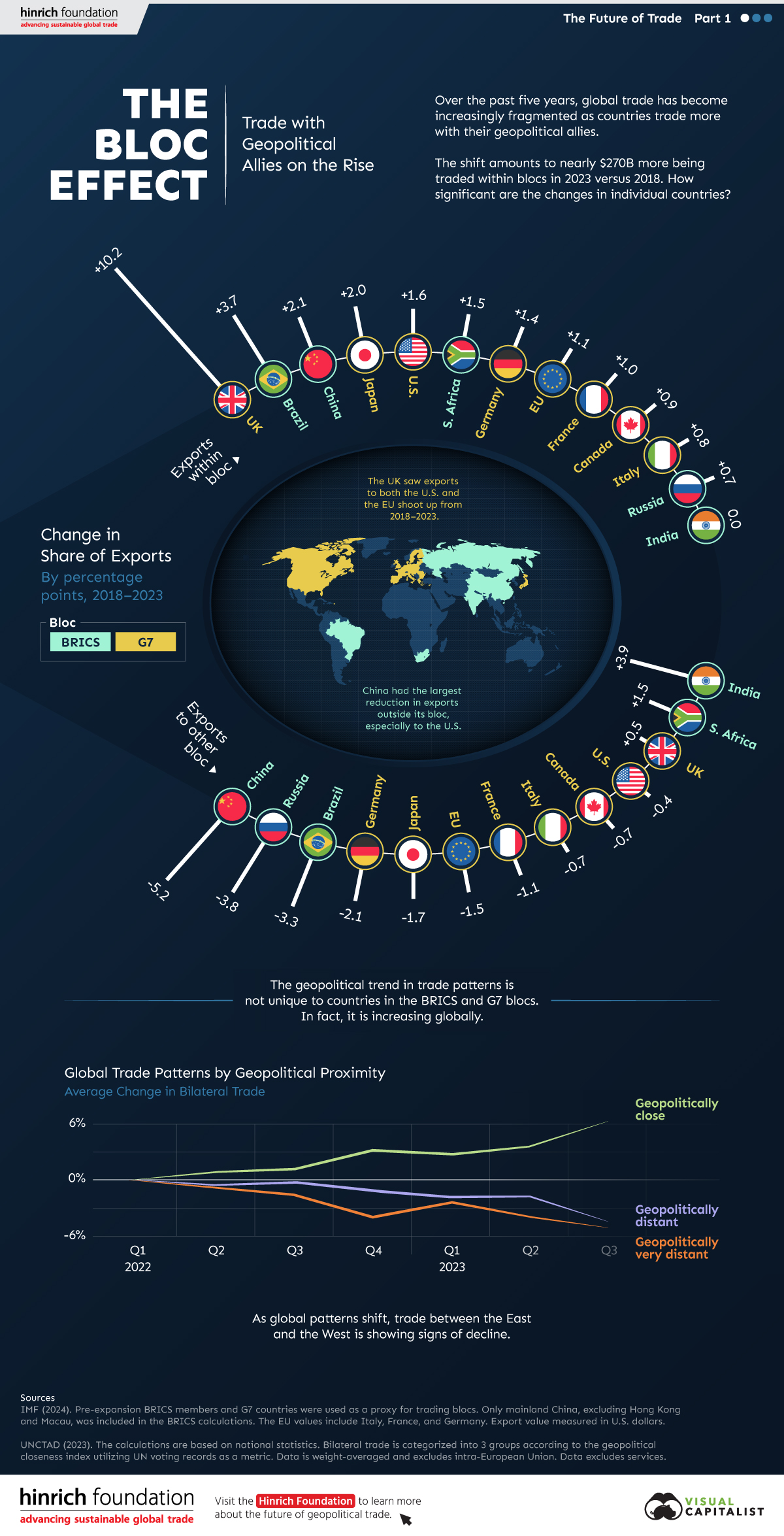
Trade Shifts in G7 and BRICS Countries
This analysis uses IMF data to examine differences in shares of exports within and between trading blocs from 2018 to 2023. For example, we looked at the percentage of China’s exports with other BRICS members as well as with G7 members to see how these proportions shifted in percentage points (pp) over time.
Countries traded nearly $270 billion more with allies in 2023 compared to 2018. This shift came at the expense of trade with rival blocs, which saw a decline of $314 billion.
Country Change in Exports Within Bloc (pp) Change in Exports With Other Bloc (pp)
🇮🇳 India 0.0 3.9
🇷🇺 Russia 0.7 -3.8
🇮🇹 Italy 0.8 -0.7
🇨🇦 Canada 0.9 -0.7
🇫🇷 France 1.0 -1.1
🇪🇺 EU 1.1 -1.5
🇩🇪 Germany 1.4 -2.1
🇿🇦 South Africa 1.5 1.5
🇺🇸 U.S. 1.6 -0.4
🇯🇵 Japan 2.0 -1.7
🇨🇳 China 2.1 -5.2
🇧🇷 Brazil 3.7 -3.3
🇬🇧 UK 10.2 0.5
All shifts reported are in percentage points. For example, the EU saw its share of exports to G7 countries rise from 74.3% in 2018 to 75.4% in 2023, which equates to a 1.1 percentage point increase.
The UK saw the largest uptick in trading with other countries within the G7 (+10.2 percentage points), namely the EU, as the post-Brexit trade slump to the region recovered.
Meanwhile, the U.S.-China trade dispute caused China’s share of exports to the G7 to fall by 5.2 percentage points from 2018 to 2023, the largest decline in our sample set. In fact, partly as a result of the conflict, the U.S. has by far the highest number of harmful tariffs in place.
The Russia-Ukraine War and ensuing sanctions by the West contributed to Russia’s share of exports to the G7 falling by 3.8 percentage points over the same timeframe.
India, South Africa, and the UK bucked the trend and continued to witness advances in exports with the opposing bloc.
Average Trade Shifts of G7 and BRICS Blocs
Though results varied significantly on a country-by-country basis, the broader trend towards favoring geopolitical allies in international trade is clear.
Bloc Change in Exports Within Bloc (pp) Change in Exports With Other Bloc (pp)
Average 2.1 -1.1
BRICS 1.6 -1.4
G7 incl. EU 2.4 -1.0
Overall, BRICS countries saw a larger shift away from exports with the other bloc, while for G7 countries the shift within their own bloc was more pronounced. This implies that though BRICS countries are trading less with the G7, they are relying more on trade partners outside their bloc to make up for the lost G7 share.
A Global Shift in International Trade and Geopolitical Proximity
The movement towards strengthening trade relations based on geopolitical proximity is a global trend.
The United Nations categorizes countries along a scale of geopolitical proximity based on UN voting records.
According to the organization’s analysis, international trade between geopolitically close countries rose from the first quarter of 2022 (when Russia first invaded Ukraine) to the third quarter of 2023 by over 6%. Conversely, trade with geopolitically distant countries declined.
The second piece in this series will explore China’s gradual move away from using the U.S. dollar in trade settlements.

Visit the Hinrich Foundation to learn more about the future of geopolitical trade

-

 Economy4 hours ago
Economy4 hours agoEconomic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024
The IMF has released its economic growth forecasts for 2024. How do the G7 and BRICS countries compare?
-

 United States1 week ago
United States1 week agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
We visualized the top U.S. companies by employees, revealing the massive scale of retailers like Walmart, Target, and Home Depot.
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
We visualized product categories that saw the highest % increase in price due to U.S. inflation as of March 2024.
-

 Economy4 weeks ago
Economy4 weeks agoG20 Inflation Rates: Feb 2024 vs COVID Peak
We visualize inflation rates across G20 countries as of Feb 2024, in the context of their COVID-19 pandemic peak.
-

 Economy1 month ago
Economy1 month agoMapped: Unemployment Claims by State
This visual heatmap of unemployment claims by state highlights New York, California, and Alaska leading the country by a wide margin.
-
 Economy2 months ago
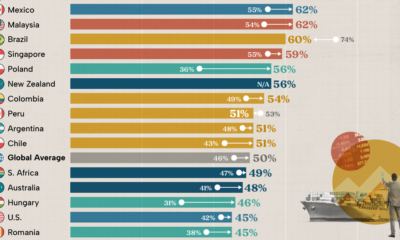
Economy2 months agoConfidence in the Global Economy, by Country
Will the global economy be stronger in 2024 than in 2023?
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023